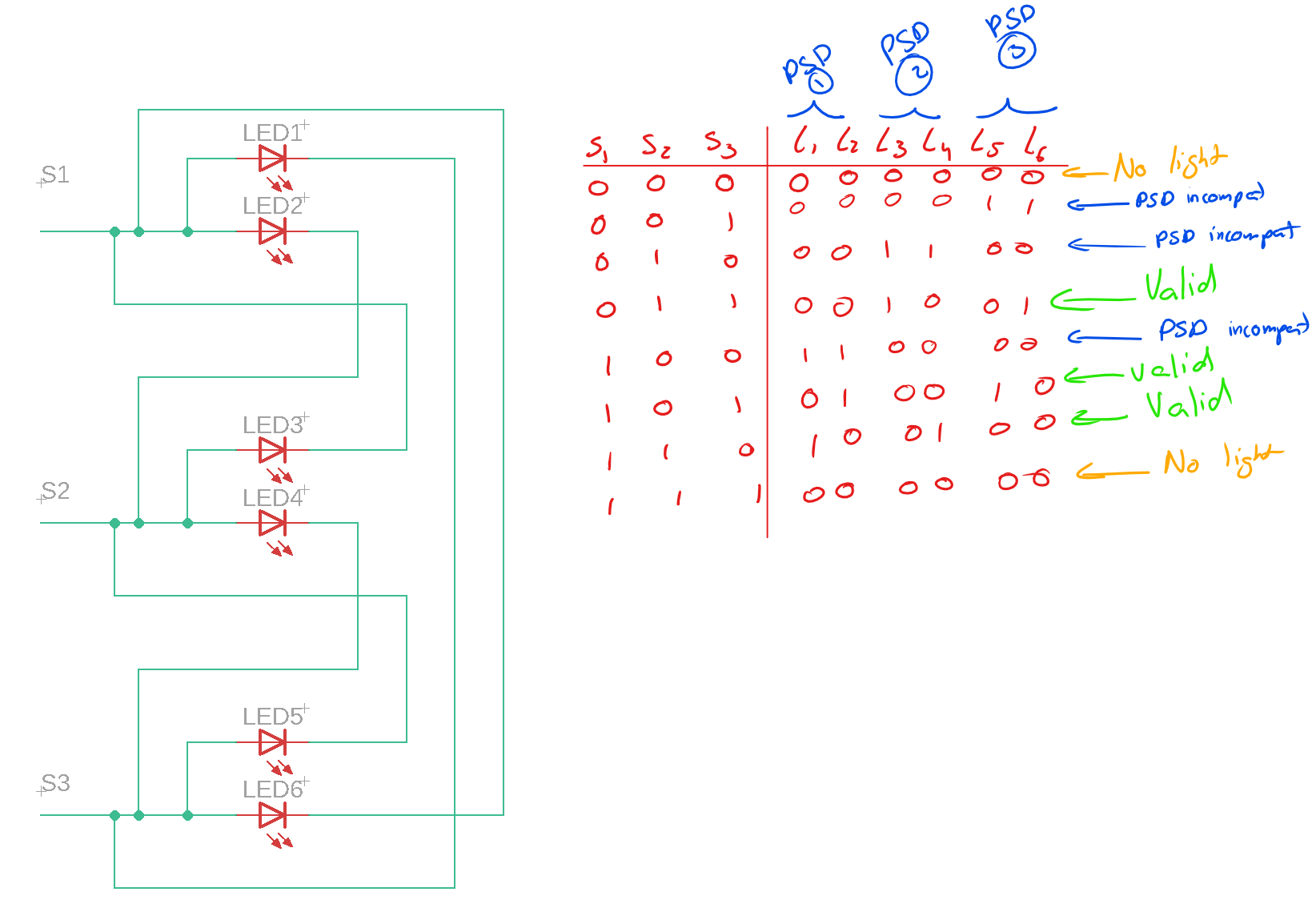
One dimensional Operation
A (1-D) PSD will output (in the form of current) the position of a light beam in a light strip. Given two linked light sources, a two degrees of freedom system can be derived. The goal is to locate the relative position of the center of both light sources with respect to the center of the PSD. i.e X_Target and Y_Target
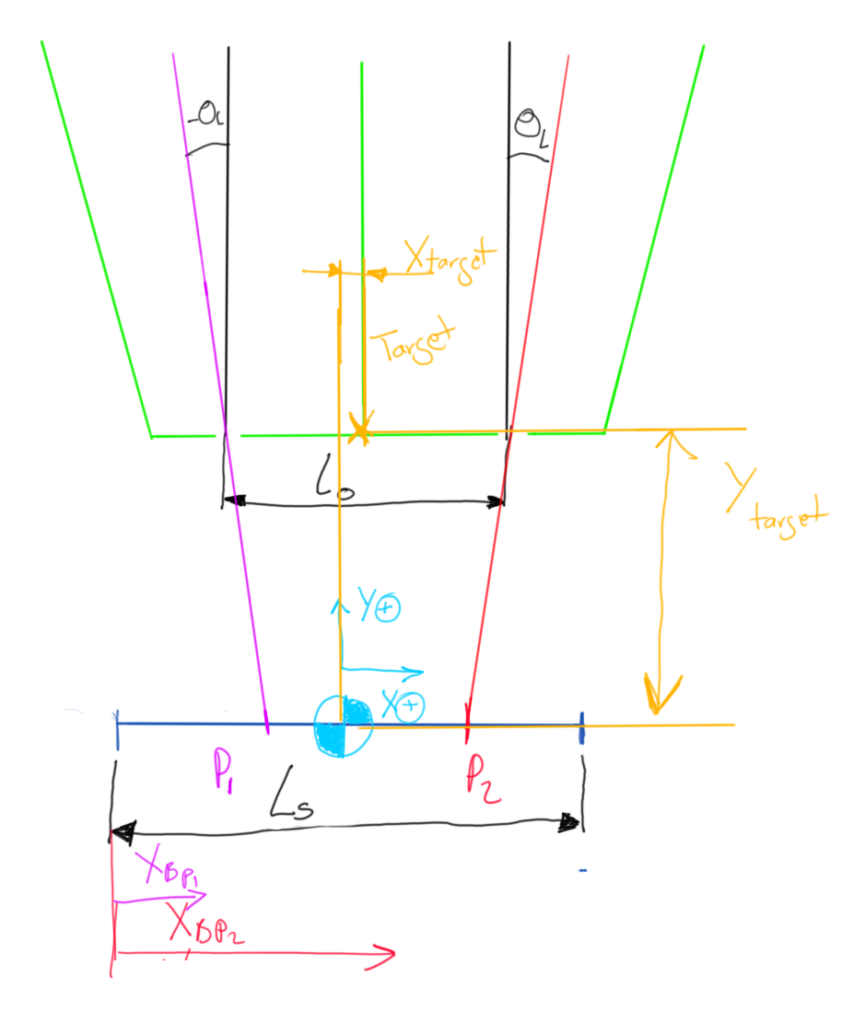
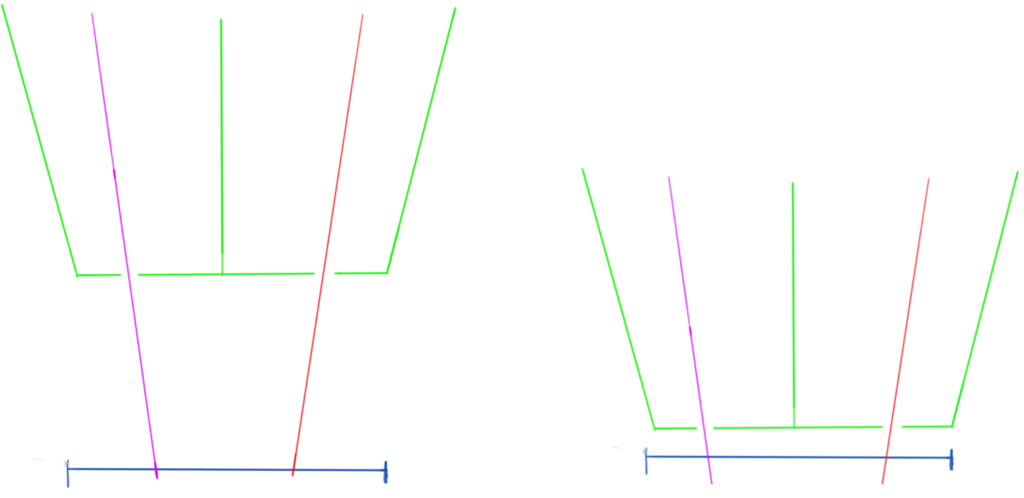
Distance to sensor
When both lights (Magenta & Red Beams) are closer, the distance between sensor and source is further away, while if both lights are closer, both lights are further apart, it, the light sources are closer to the sensor
The equation to find the distance to the sensor would be:
Y_t=L0-(XbP2-XbP1)/(2*tan(theta_L))
Position relative to sensor
The relative position is the average between both positions. This distance will be referenced from the center
X_t=(XbP1+XbP2-Ls)/2
Tree dimensional Operation
First of all, lets first define the frame of reference we will be using to determine the position
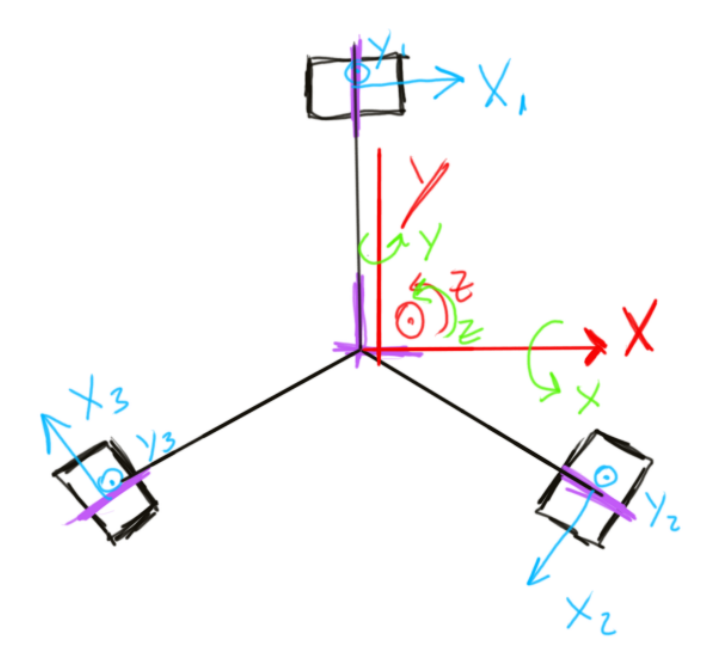
The goal is to determine the three translations and three rotations that define the position of the joystick
Translations
X direction
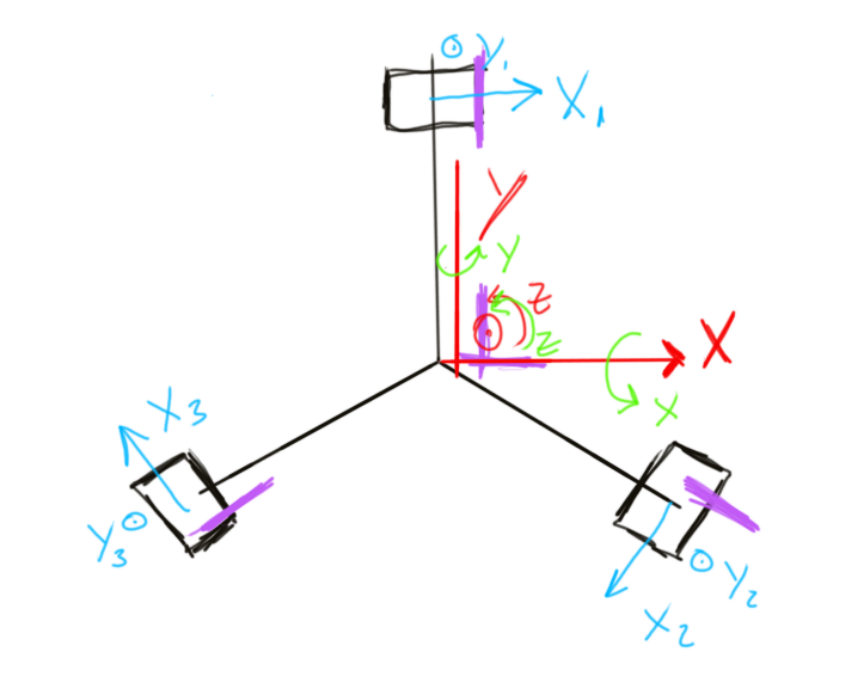
In the X direction we will average the translation of the three sensors
X=(X1*cos(90)+X2*cos(210)+X3*cos(-30))/3
Y direction
In the Y direction, sensor #1 will not see any change, therefore the equation will be as follows
Y=(X3*Sin(-30)-X2*Sin(210))/2
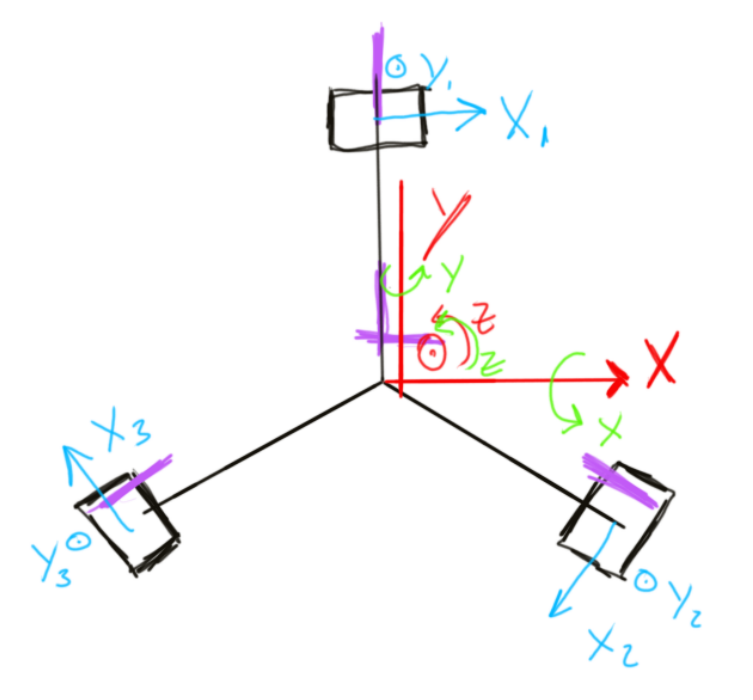
Z Direction
For The Z direction, the distance will be the average between the vertical directions of each sensor
Z=(Y1+Y2+Y3)/3
Rotations
Rotation around X
Around the X-axis, Sensor 2 and sensor 3 will see the same distance;
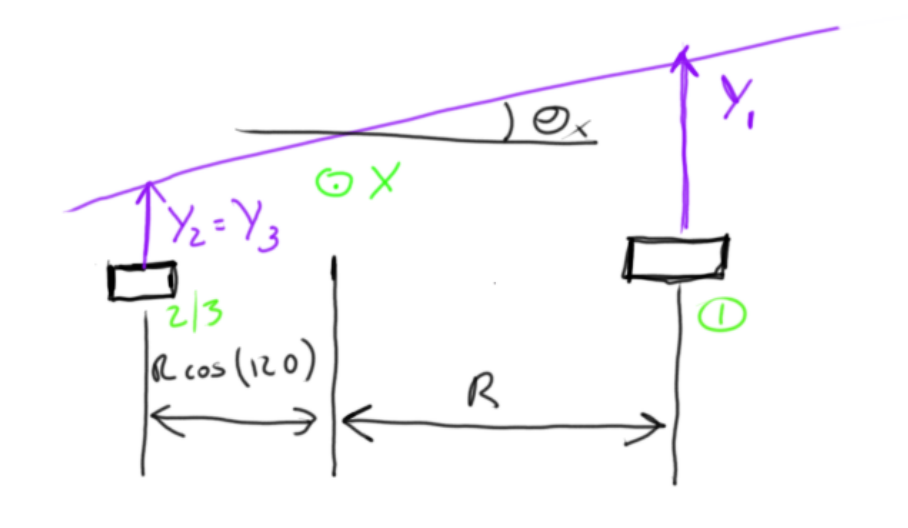
The equation will be:
Theta_X=tan^-1((Y1-((Y2+Y3)/2)))/(R+R*cos(120)))
Rotation around Y
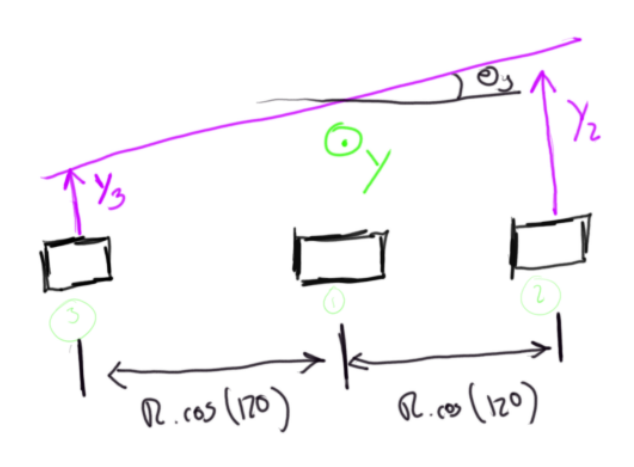
The rotation around the Y axis will be:
Theta_Y=tan^-1((Y2-Y3)/(2*R*cos(120)))
Rotation around Z
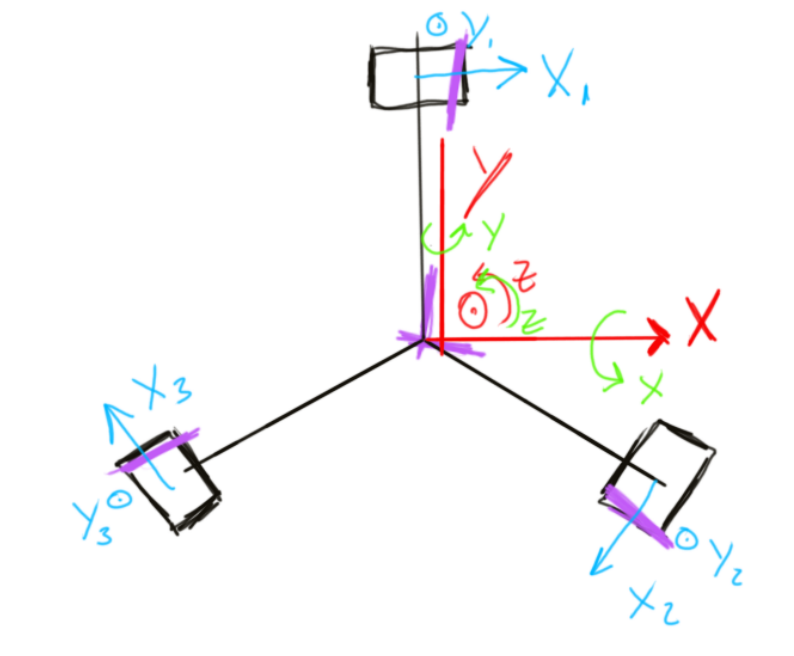
The rotation around the Z axis will be:
Theta_Z=tan^-1 (((-X1-X2-X3)/3)/R)